Immuno-Diagnostics Antibodies and Antigens for Huntington's Disease (HD)
What is Huntington's Disease (HD)?
A CAG repeats expansion mutation of the HTT gene leading to the abnormal accumulation of the mutant huntingtin protein (mHTT) is a hereditary rare neurodegenerative disorder [1-2].
Pathological Changes
Huntington’s disease (HD) consists of a continuous succession of deteriorating neurological conditions. Neuronal degeneration is observed to be concentrated in the striatum and cortical areas and affects motor coordination, cognition, and mood. It is proteinopathy consequent to a HTT gene mutation that results in the production of a mutant huntingtin protein (mHTT), which is toxic to neurons and forms intracellular aggregates. These inclusions impair synaptic protein degradation, cellular energy production, and transcription leading to exacerbation of neuronal pathology. HD also affects neurotransmitter homeostasis: glutamate and GABA and leads to chorea and cognitive dysfunction. Chronic neurodegeneration results eventually in overall cerebral volume reduction and atrophy involving primarily the striatum and the cortex as confirmed in three respective studies.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Huntington’s disease (HD) can be made based on clinical examination and some specific examinations. A neurological examination assesses motor signs including chorea, and rigidity in addition to alterations in cognitive function and psychiatric symptoms. Molecular diagnosis is always the most accurate one and in the case of HJTS it is based on a detection of an abnormal CAG repeat expansion of the HTT gene. Neuropsychological tests bring information regarding the changes on memory, attention, and emotional functioning as an addition to the clinical picture. MRI or CT scans can produce pathognomonic atrophic changes in striatum and cortex, which contribute to the diagnosis of the disease and evaluation of the course. Also, there are biomarker tests that are undergoing trials in diagnosing the disease in the early stages, and monitoring the disease progress are the levels of mutant huntingtin in liquefied around the spinal cord or in the blood. In combination, these methods provide basis for through and reliable assessment of HD.
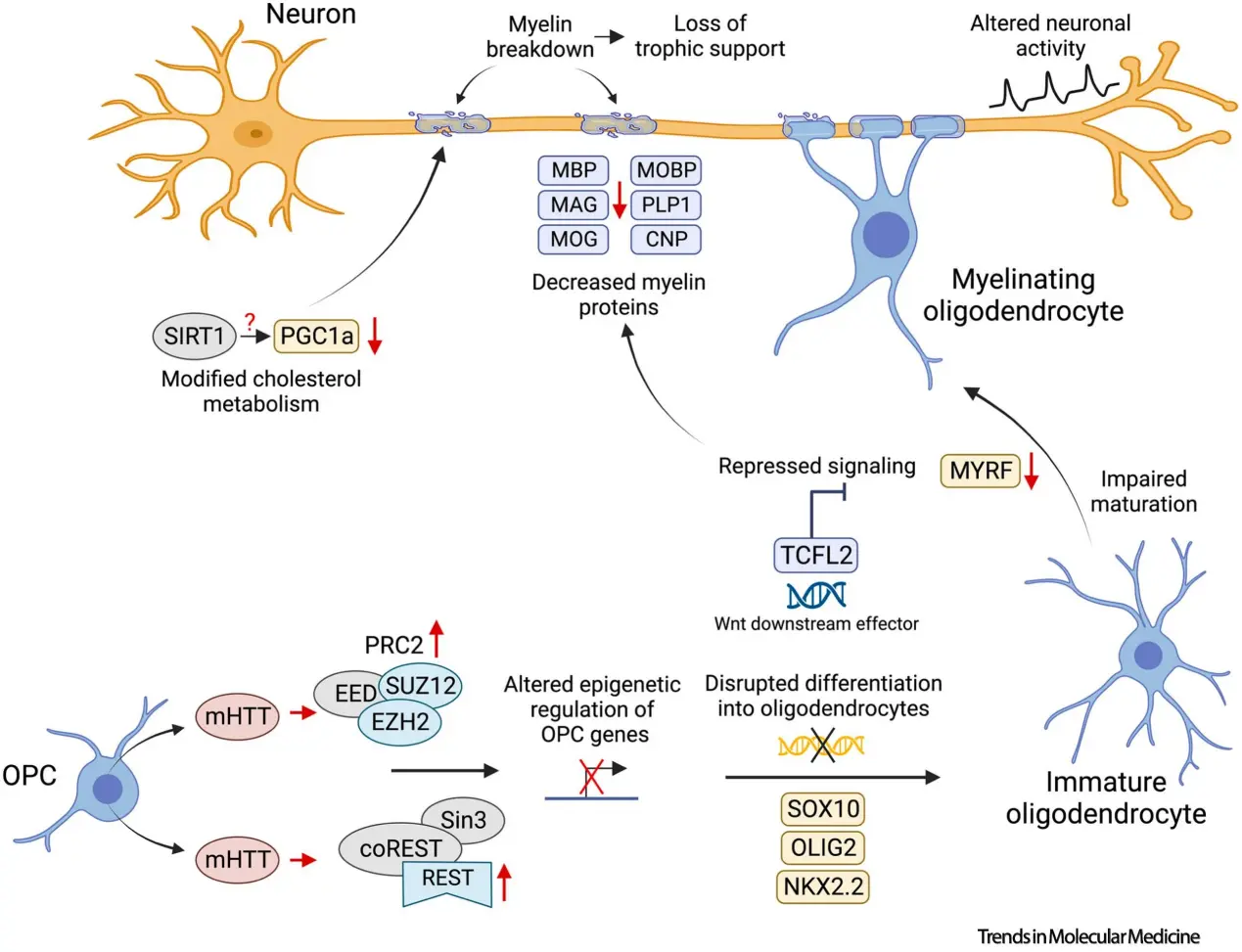
Figure 1. Oligodendrocyte pathology in Huntington's disease: from mechanisms to therapeutics by Costanza Ferrari Bardile / Source: sciencedirect.com
Biomarkers for Huntington's Disease
| Biomarker | Limit (Pathological concentration in blood) |
|---|---|
| Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) | / |
| Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1/CCL2) | / |
| Interleukin-6 (IL-6) | / |
| Neurofilament light chain (NfL) | / |
| Pro-neuropeptide Y | / |
Sample Types: Blood, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)






 Full
List Download
Full
List Download