Anti-MMAE/MMAF payload antibody in PK study in ADC drug development
PKs are important in ADC drug development since it gives the understanding of the behavior in the body of the ADC, the antibody, the linker, and cytotoxic drug. In the case of ADCs employing monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) or monomethyl auristatin F (MMAF) as the cytotoxic agents, ant- MMAE or ant- MMAF Abs can be of great value.
| Cat No. | Product Description | Fc | Products Information |
| GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-01 | Anti-MMAE/MMAF monoclonal antibody | hFc/mFc | Details |
| GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-02 | Anti-MMAE monoclonal antibody | hFc/mFc | Details |
Application
Competitive immunoassay validation (Competitive
ELISA) and other Immunoassay,
PK & PD assay for MMAE payload of Antibody-drug Conjugate (ADC)
Highlight:
Purity: ≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
High affinity
and specificity validated
High sensitivity verified by ADCs binding assay
GeneMedi's GMP-Bios-Auristatin-Ab: Precision Binding with MMAE and MMAF-Based ADCs
As a result, GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-01-2 expressed by GeneMedi has significant complementarity with ADCs containing MMAE or MMAF payloads due to its ability to bond with both. Conversely, GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-02-2 provides selective acknowledgement to MMAE-based ADCs and has a lower impact on other targets. Moreover, out of the two, neither bounded with ADCs conjugated with DXD; such a move from GeneMedi aims at providing enhanced highly selective antibodies that offer ideal therapeutic performance.
- Figure 1: Coating PTM-1 MMAE
- Figure 2: Coating PTM-1 MMAF
- Figure 3: Coating PTM-1 DXD
- Figure 4: Pharmacokinetic (PK) studies

Figure 1. GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-01-2 and GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-02-2 have been actively bound with the ADC (PTM-1 MMAE).
Figure 1 demonstrates the efficacy of
GeneMedi's GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-01-2
and GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-02-2 in
actively binding with the ADC (PTM-1 MMAE). This underscores GeneMedi's
commitment to
producing
high-quality antibodies tailored for effective conjugation with MMAE-based ADCs.
The robust
binding
displayed in the figure highlights GeneMedi's expertise in developing antibodies
optimized
for
targeted drug delivery, a critical aspect in the field of antibody-drug
conjugates.

Figure 2. The GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-01-2 has been actively bound with the ADC (PTM-1 MMAF). While GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-02-2 has not been bound with the ADC with MMAF.
In Figure 2, the specificity of
GeneMedi's antibodies is showcased
as GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-01-2 successfully
binds with the ADC (PTM-1 MMAF), while GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-02-2 remains unbound. This
specificity
is
pivotal in ensuring precise targeting of MMAE-containing ADCs, enhancing their
therapeutic
efficacy
while minimizing off-target effects.
GeneMedi's ability to tailor antibodies to selectively
bind
with distinct drug payloads exemplifies their proficiency in antibody
engineering, offering
researchers reliable tools for precision medicine applications.

Figure 3. GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-01-2 and GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-02-2 have not been bound with the ADC conjugated with DXD.
Figure 3 illustrates another aspect
of GeneMedi's antibody
specificity, revealing that neither
GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-01-2 nor GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-02-2 binds with the ADC conjugated with
DXD. This data
underscores GeneMedi's dedication to producing antibodies with high selectivity,
ensuring
minimal
interference with undesired payloads.
By providing antibodies that exhibit minimal
cross-reactivity,
GeneMedi empowers researchers with precise tools for designing and optimizing
ADCs for
targeted
cancer therapy, ultimately advancing the forefront of biomedical research and
clinical
applications.
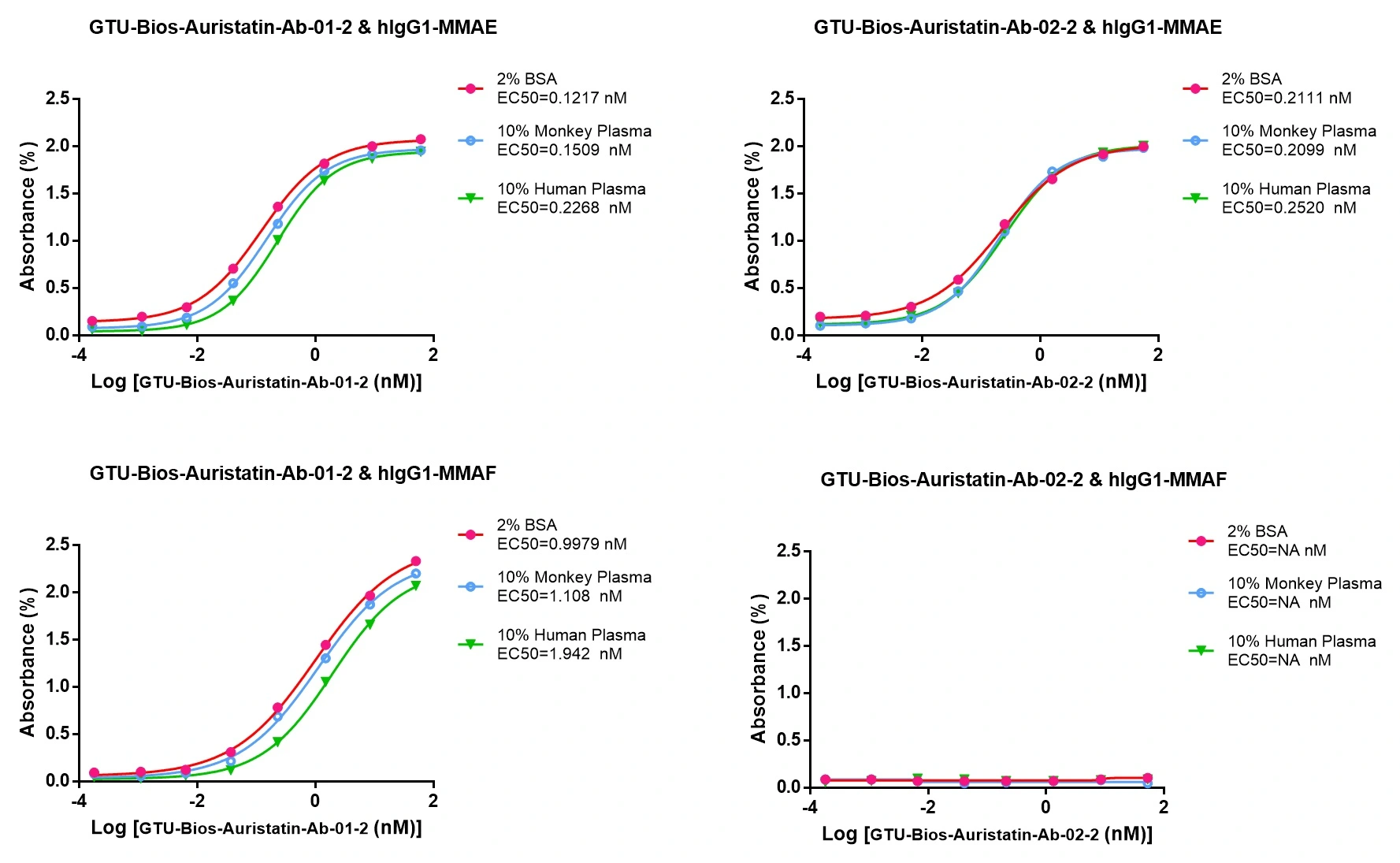
Figure 4: GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-01-2 and GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-02-2 can be used in pharmacokinetic (PK) studies involving humans and monkeys
GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-01-2 has minimal impact in human and monkey PK studies and can be considered negligible. GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-02-2 has even less impact than GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-01-2 in these PK studies. Both GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-01-2 and GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-02-2 are suitable for use in human and monkey PK experiments.
Role of Anti-MMAE/MMAF Antibodies in PK Studies
-
Detection and Quantification:
-
Limitations in detecting the amount of MMAE/MMAF levels that circulate in the bloodstream or are released from an ADC are corrected by using Anti-Madden-ACA/MMAF antibodies. This is helpful in determining the stability of the ADC that has been formed, and the rate that the drug is being released.
-
-
Assessing ADC Integrity:
-
Using these antibodies, researchers can then assay the free MMAE/MMAF levels in circulation where an estimation of the linker stability can be deduced from. It might essentially mean that the free drug concentration is higher and the stability of the linker is lower, thereby promoting the release of the cytotoxic drug.
-
-
Safety and Efficacy Correlation:
-
Understanding the pharmacokinetics of MMAE/MMAF is also useful in determining the association between the concentration of the drug administered and the efficacy and toxicity. It is further assisted by the availability of specific Anti-MMAE/MMAF antibodies which enable measurement of the drug in various biological matrices with high accuracy.
-
-
Immunogenicity Testing:
-
Some ADCs can provoke immune response, resulting in existence of corresponding ADAs that could interfere with the drug’s efficacy and safety. As for the specific directions, it is possible to use the presence of Anti-MMAE/MMAF antibodies to distinguish between the drug per se and ADAs.
-
Application in ADC Drug Development
-
-
Preclinical and Clinical Development: In the preclinical and clinical stages, Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay or ELISA is employed to assess the drug’s partition, metabolism, and excretion with the help of anti-MMAE/MMAF antibodies. This information is critical in dosing regimen adjustment and the need to record the right dose that delivers the most therapeutic effect without harm.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Information obtained from such studies is indeed useful in meeting the regulatory needs of the drug by offering full profiles of how the drug is likely to behave in the body, which is vital for approval.
-
Formulation Optimization: Towards this end, PK studies help in obtaining valuable formualtion optimization data for the ADC. For example, if MMAE/MMAF releases before the desired time, adaptations to the linker structure or the antibodies can be made.
-
Anti-MMAE/MMAF antibodies are, therefore, essential for PK in the development of MMAE/MMAF-based ADCs as this means a comprehensive body of information that is highly influential in most courses of ADC drug development ranging from the basic research stage to the clinical stage.






