Anti-DXd/Exatecan payload antibody in PK study in ADC drug development
Rat model PK studies utilizing anti-DXD/Exatecan antibodies to measure the concentrations of DXD in ADCs involves similar machineries as there are other payload-specific antibodies such as anti-DM1/DM4. DXD is the derivative of Exatecan and the drug that acts as topoisomerase I inhibitors and used in ADCs to apply targeted therapy in cancer treatment. Several promising antibody types have been identified and their role and the methods of utilization in PK studies of both, developed and potential ADCs are significant in the overall process.
| Cat No. | Product Description | Fc | Products Information |
| GTU-Bios-DXd-Ab | Anti-DXd/Exatecan monoclonal antibody (mAb) | hFc/mFc | Details |
| GTU-Bios-Exatecan-Ab | Anti-Exatecan (Exatecan Mesylate) monoclonal antibody (mAb) | hFc/mFc | Details |
Application
Competitive immunoassay validation (Competitive
ELISA) and other Immunoassay,
PK & PD assay for MMAE payload of Antibody-drug Conjugate (ADC)
Highlight:
Purity: ≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
High affinity
and specificity validated
High sensitivity verified by ADCs binding assay
GeneMedi's GTU-Bios-DXd-Ab: Specific Binding with DXd
GeneMedi's GTU-Bios-DXd-Ab demonstrates robust binding affinity with ADCs incorporating DXd payload, highlighting its versatility. Furthermore, neither GTU-Bios-DXd-Ab shows binding with ADCs conjugated with SN38, emphasizing GeneMedi's commitment to producing highly selective antibodies tailored for optimized therapeutic outcomes.
- DXd
- Exatecan

Figure 1. GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-01-2 and GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-02-2 have not been bound with the ADC conjugated with DXD.
Figure 4 illustrates another aspect
of GeneMedi's antibody
specificity, revealing that neither
GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-01-2 nor GTU-Bios-Auristatin-Ab-02-2 binds with the ADC conjugated with
DXD. This data
underscores GeneMedi's dedication to producing antibodies with high selectivity,
ensuring
minimal
interference with undesired payloads.
By providing antibodies that exhibit minimal
cross-reactivity,
GeneMedi empowers researchers with precise tools for designing and optimizing
ADCs for
targeted
cancer therapy, ultimately advancing the forefront of biomedical research and
clinical
applications.
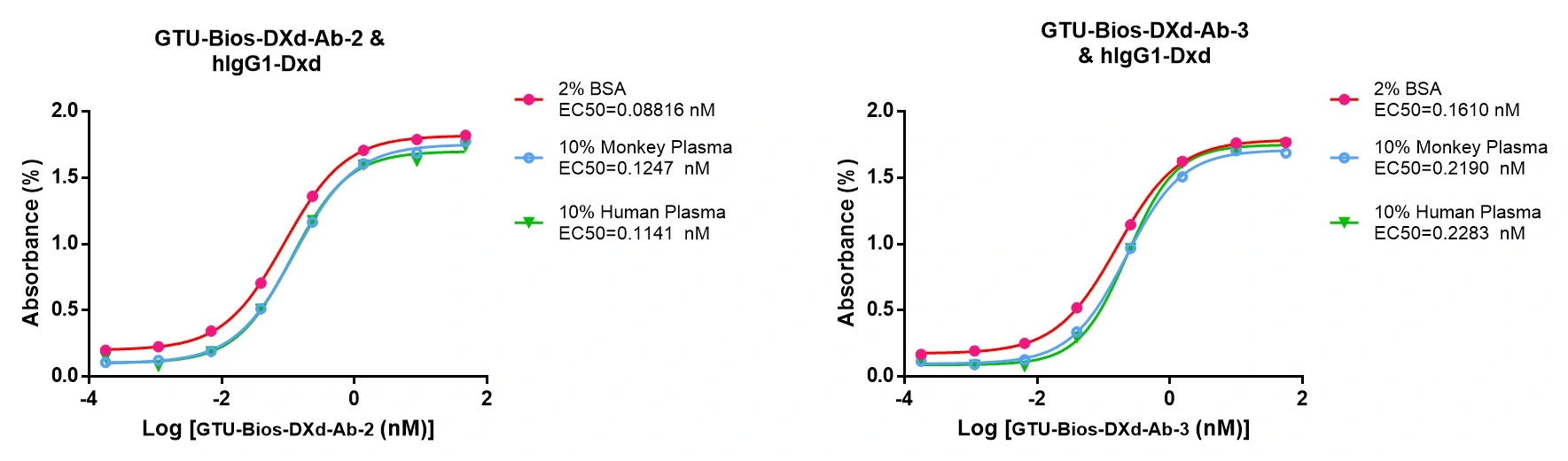
Figure 2. GTU-Bios-DXd-Ab has minimal impact on pharmacokinetic (PK) studies involving humans and monkeys.
GTU-Bios-DXd-Ab demonstrates minimal influence in PK studies with humans and monkeys, rendering it appropriate for application in these experiments.
GeneMedi’s Anti-Exatecan Antibodies Exhibit High Specificity
GeneMedi's GTU-Bios-Exatecan-Ab demonstrates specific binding affinity for Exatecan ADCs, highlighting its functional efficacy. Furthermore, its lack of binding to SN38-conjugated ADCs emphasizes GeneMedi's dedication to developing highly selective antibody solutions.
Figure 3. GeneMedi's GTU-Bios-Exatecan-Ab: Specific Binding with Exatecan, Not Binding with SN38.
A. Exatecan ADC binding activity assay results show that the EC50 of GTU-Bios-Exatecan-Ab-2 is 0.06271 nM, while the EC50 of GTU-Bios-Exatecan-Ab-3 is 0.07254 nM, indicating strong binding affinity for Exatecan ADC.
B. Both GTU-Bios-Exatecan-Ab-2 and GTU-Bios-Exatecan-Ab-3 are not available (N.A.) in the SN38 ADC binding assay.

Why Use Anti-DXD/Exatecan Antibody in ADC drug development?
-
Accurate Payload Quantification: anti-DXD/Exatecan antibodies prevent the accurate determination of how much DXD is bound to the antibody throughout the drug’s lifetime in the body and in the circulation. This measurement is critical in establishing the capacity and efficiency of the drug being used and its impact on the users.
-
Stability Assessment: Such fast deconjugation rates can be used to know the stability of the DXD payload bound to the antibody across time scales. This data is instrumental in determining the optimal formulation and storage conditions of the therapeutic molecule that is the ADC.
-
Detailed Pharmacokinetics: This allows the specific pharmacokinetics of the entire ADC, as well as and the free DXD payload, to be discerned when PK measurements are undertaken with anti-DXD/Exatecan antibodies. This separation is essential when considering the actions and fates of the drug, including its distribution, metabolism, elimination and toxic effects that may ensue if they are encountered in the body.
-
Biodistribution Analysis: They are also used to evaluate biodistribution of the ADC, or the location of the drug and its payload in the body, thus it is used to depict the targeting effectiveness and the possible harm to the other organs.
How to use Anti-DXD/Exatecan Antibody in ADC drug development?
-
Immunoassays: The two most widely employed techniques for quantifying and or determining the binding affinity of anti-DXD/Exatecan antibodies in PK studies are mostly those immunological assays that include the ELISA. These assays are able to accurately and selectively identify and measure the concentration of the DXD-conjugated antibody in the blood plasma or other biological fluids, and thus collect useful information on the ADC level at different time points.
-
Immunohistochemistry: In tissue analysis, anti-DXD/Exatecan antibodies are beneficial since they are happy to identify the quantity and position of the ADC in tissues, principally in tumor cells. This aid in the assessing of the efficiency of ADC to achieve the right tumor site and invade the surrounding milieu.
-
Mass Spectrometry Support: Although, anti-DXD/Exatecan antibodies are not employed for direct MS applications, they can be deployed in preparative steps for isolation and or concentration of ADCs or free payload from cocktail biomatrix before their MS analysis. This enhances the signal-to-noise ratio and accuracy of the MS measurements.
-
Assay Development: anti-DXD/Exatecan antibodies play a crucial role in the creation and validation of sensitive, accurate, and reproducible assay for the efficacy studies across the preclinical and early-phase clinical ADC development.
By employing diet-mate charge switching reagents, such as anti-DXD/Exatecan antibodies in PK studies, researchers can know the pharmacokinetics and dynamics of the ADC to perfect its formulation, therapeutic dosing, and side effects. DXD is one of the most promising platforms in ADC therapies, and therefore this detailed evaluation of its effectiveness is of paramount importance for optimizing the development of this therapeutic platform, to directly benefit from its potential in delivering targeted drugs with minimal side effects, and indirectly contribute to the approval of DXD-derivatives by different regulatory authorities.






