PCT(Procalcitonin) in Veterinary Diseases: A New Frontier in Diagnosis
The main advantage of PCT is that it is increased repeatedly during systemic bacterial infection, which makes it possible to establish the diagnosis of sepsis and orient the choice of antibiotics.
| Catalog No. | Products Name | Detected Species | Products Information |
| GMP-BOV-CRP-Ag01 | C-Reactive Protein | Bovines/Cattle | Details |
| GMP-BOV-PCT-Ag | PCT | Bovines/Cattle | Details |
| GMP-BOV-PCT-Ab | Anti-Bovine PCT monoclonal antibody (mAb) | Bovines/Cattle | Details |
| GMP-CAN-PCT-Ag | PCT | Dog/Canine | Details |
| GMP-CAN-PCT-Ab | Anti-Canine PCT monoclonal antibody (mAb) | Dog/Canine | Details |
| GMP-EQU-PCT-Ag | PCT | Equine/Horse | Details |
| GMP-EQU-PCT-Ab | Anti-Equine PCT monoclonal antibody (mAb) | Equine/Horse | Details |
| GMP-FEL-PCT-Ag | PCT | Cat/Feline | Details |
| GMP-FEL-PCT-Ab | Anti-Feline PCT monoclonal antibody (mAb) | Cat/Feline | Details |
What is Procalcitonin? Understanding Its Role in Veterinary Medicine
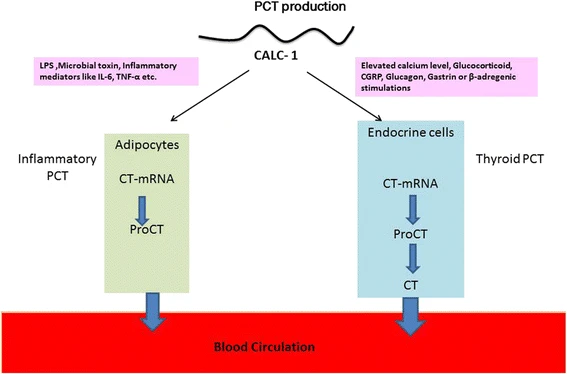
For animals, there is procalcitonin (PCT) which is being investigated as another promising marker to be used in diagnosing systemic bacterial infections and sepsis. PCT is an inactive polypeptide that is converted into the hormone calcitonin that is primarily secreted by the thyroid C cells but in view of a generalized infection PCT could significantly increase in all the tissues. It has been proved that PCT is the potent biomarker of bacterial infection and their intensity in the humans, which increases in septic and severe bacterial infection but not in the viral and noninfectious inflammatory disorders.
Unlocking the Potential: Diseases Detected by PCT in Animals
Research on using PCT in veterinary medicine in terms of a diagnostic marker is of emerging interest; studies investigated its value in diagnosing different animal species ranging from dogs, cats, and horses and etc. The rationale is that as with people, abnormal high PCT levels in animals could point to a bacterial infection or sepsis, which in turn, could help when deciding on the use of antibiotics.
Potential Applications of PCT in Animals:
(1) Identifying Bacterial Infections: Increased PCT means that one can be able to differentiate between bacterial infections and viral diseases and so able to decide whether or not to use an antibiotic.
(2) Diagnosing Sepsis: PCT level could be elevated in the case of sepsis that requires immediate treatment.
(3) Monitoring Treatment Response: It was found that the fluctuation of the PCT levels can be applied for monitoring and evaluation of the treatment of bacterial infection and sepsis.
Research and Limitations:
The objective of using PCT as a biomarker in animals has the numerous potentiality’s but the research on this subject area is yet in its developmental stage. To this end, researches conduct efforts to set species-specific reference targets for PCT, to determine the pattern of PCT changes in response to infections in different animals and to design cheap and accurate analyses usable in veterinary medicine. At present, the possibilities of PCT application in diagnosing various diseases in veterinary medicine are precluded by these factors, and PCT does not have as great demand as some other markers of inflammation like CRP.
Thus, PCT is a promising biomarker to diagnose bacterial infections and sepsis in animals, however, it is still required more investigations to identify its benefits and drawbacks to veterinary medicine.
| Animals | Possible Diseases Listed | Specimens/Biofluids | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dog | Bacterial Sepsis, Systemic Infections, Acute Pancreatitis, Pyometra | Blood | Immunoassay |
| Cat | Bacterial Sepsis, Systemic Infections, Feline Infectious Peritonitis (FIP) | Blood | Immunoassay |
| Horse | Bacterial Sepsis, Neonatal Septicemia, Acute Abdominal Disorders | Blood | Immunoassay |
| Cattle | Bacterial Sepsis, Neonatal Septicemia, Metritis, Mastitis | Blood | Immunoassay |






